Introduction
The use of robotics in agriculture is of great importance in maximizing productivity and efficiency. In Nigeria, the agricultural sector plays a crucial role in the economy.
With a population of over 200 million people, Nigeria’s agricultural sector is vital for food security and job creation.
However, it faces various challenges such as outdated techniques and inadequate manpower.
Robotic technology can revolutionize Nigeria’s agricultural sector by addressing these challenges.
By automating tasks such as planting, harvesting, and irrigation, robotics can significantly increase productivity and reduce labor costs.
Furthermore, robotics can improve the accuracy and precision of agricultural processes, ensuring optimal use of resources and minimizing waste.
This is particularly important in a country like Nigeria, where land and water resources are limited.
The introduction of robotics in Nigeria’s agricultural sector also presents opportunities for innovation and entrepreneurship.
It can attract young entrepreneurs and tech-savvy individuals to invest in agriculture, leading to the development of new and sustainable farming practices.
Moreover, robotics can enhance the safety and well-being of farmers. By taking over physically demanding and hazardous tasks, robots can prevent injuries and improve overall working conditions.
In summary, the integration of robotics in Nigeria’s agricultural sector holds immense potential. It can address the sector’s challenges, improve productivity, and encourage innovation.
Embracing robotics in agriculture will not only benefit Nigeria’s economy but also ensure food security for its growing population.
The Current State of Nigeria’s Agricultural Sector
The agricultural sector in Nigeria is currently facing numerous challenges that need to be addressed. Nigerian farmers encounter a range of obstacles that hinder their productivity and profitability.
Additionally, there is a pressing need for technological advancements to boost the sector’s efficiency and sustainability.
Challenges faced by Nigerian farmers
- Poor infrastructure: Nigerian farmers often struggle with inadequate road networks, which impede their ability to transport goods to markets.
- Inadequate access to credit: Many farmers lack access to affordable loans and credit facilities, making it challenging for them to invest in modern farming techniques and equipment.
- Limited access to modern agricultural inputs: The availability of improved seeds, fertilizers, and pesticides remains limited in many rural areas, affecting crop yields.
- Inefficient farming techniques: Traditional farming methods are still prevalent in many parts of Nigeria, leading to low productivity and waste.
- Inconsistent power supply: Frequent power outages hinder the use of machinery and technology, reducing overall efficiency.
- Inadequate storage facilities: The absence of proper storage facilities leads to post-harvest losses due to spoilage and pest infestation.
- Poor market access: Many farmers struggle to access formal markets due to distance, lack of information, and market inefficiencies.
- Climate change impacts: Unpredictable weather patterns, including irregular rainfall and extreme temperatures, affect crop growth and livestock rearing.
- Limited government support: Insufficient investment in agricultural research, extension services, and farmer education contributes to the sector’s challenges.
Need for technological advancements
- Enhanced farm mechanization: Introducing modern machinery and equipment can improve efficiency and reduce labor-intensive farming practices.
- Precision agriculture: Utilizing technologies such as drones, sensors, and GPS can optimize resource usage, enhance productivity, and reduce environmental impacts.
- Access to information and markets: Digital platforms and mobile applications can provide farmers with real-time market prices, weather forecasts, and best practices.
- Improved irrigation systems: Efficient irrigation techniques, including drip irrigation and precision watering, can help optimize water usage and mitigate the impact of water scarcity.
- Post-harvest management solutions: Investments in cold storage facilities, packaging innovations, and food processing can reduce post-harvest losses and improve product quality.
- Climate-smart technologies: Adopting climate-resilient crop varieties, improved soil management techniques, and renewable energy sources can mitigate the effects of climate change.
- Financial technology solutions: Digital payment systems, mobile banking, and insurance services can promote financial inclusion and provide farmers with easier access to credit.
- Capacity building: Investment in agricultural education, training programs, and extension services is crucial in equipping farmers with knowledge and skills.
- Public-private partnerships: Collaboration between the government, agricultural organizations, and technology providers can drive innovation and create an enabling environment.
In summary, Nigeria’s agricultural sector faces several challenges, ranging from poor infrastructure to limited access to credit and technologies.
Implementing technological advancements can help overcome these challenges and pave the way for a more efficient and sustainable agricultural sector in Nigeria.
Introduction to Robotics in Agriculture
Nigeria’s agricultural sector is pivotal to its economy, yet constrained by resource limitations and population growth.
Innovation is vital for enhanced productivity. Robotics has emerged as a promising solution.
Agricultural robotics, or agri-robots, employ automation for tasks like planting, harvesting, and monitoring crops, streamlining operations, reducing costs, and boosting productivity.
Globally, successful instances include robotic milking, revolutionizing dairy farming by automating milking and health monitoring.
Drones equipped with advanced imaging aid precision agriculture, optimizing irrigation, fertilization, and pest control.
Autonomous harvesting robots delicately pick produce, minimizing damage and saving labor. Livestock management benefits from robots automating feeding, monitoring, and waste cleaning.
Nigeria, with its reliance on agriculture, can benefit significantly from agri-robots. These technologies combat labor shortages, lower costs, and enhance productivity.
Embracing robotics can transform Nigeria’s agriculture, ensuring food security, provided stakeholders invest in research, development, and training.
Robotics in Nigeria’s Agricultural Sector
Robotics technology has gained significant adoption and utilization in Nigeria’s agricultural sector, revolutionizing various processes and improving overall productivity.
A. Current Adoption and Utilization of Robotics
- Robots are being employed for seeding, planting, and harvesting crops, reducing labor-intensive tasks.
- Automated drones equipped with sensors and cameras are used for crop monitoring and pest control.
- Robotic milking machines have increased milk production efficiency and reduced manual labor in dairy farms.
- Intelligent robots assist with animal husbandry, including monitoring livestock health and feeding.
- Agricultural robots are employed in soil analysis, precise irrigation, and fertilizer application, optimizing crop yields.
- Robotic sorting systems enhance post-harvest processes, improving the quality of agricultural produce.
B. Initiatives and Projects Involving Robotics
- The Nigerian Institute of Agricultural Engineering (NIAE) actively promotes the integration of robotics in agriculture.
- Under the NIAE, the Robotic Farming Technology Research Group conducts research and development in agricultural robotics.
- The Robotics and Artificial Intelligence Nigeria (RAIN) initiative focuses on applying robotics in various sectors, including agriculture.
- RAIN conducts training programs and workshops to educate farmers and agricultural workers about the benefits of robotics.
- The National Centre for Robotics and Artificial Intelligence Nigeria (NCRAIN) supports innovative projects in robotics and AI in agriculture.
- NCRAIN collaborates with universities, research institutions, and government agencies to promote robotics adoption and knowledge exchange.
- The Federal Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development invests in robotic farming initiatives to modernize the sector.
- Private companies, such as Farmcrowdy and Thrive Agric, are utilizing robotics and automation to enhance farming practices and support smallholder farmers.
Robotics in Nigeria’s agricultural sector has tremendous potential to address challenges such as labor shortages, post-harvest losses, and increasing food demands.
The continued adoption of robotics technology and the support of various initiatives facilitate its integration into farming practices.
The utilization of agricultural robots improves efficiency, reduces production costs, and enhances overall productivity.
By automating repetitive tasks, farmers can focus on more strategic activities, leading to increased profitability and sustainable agricultural practices.
The ability to monitor crops, soil conditions, and livestock health facilitates proactive measures to optimize yields and minimize losses.
However, challenges such as high initial costs, limited access to training and technical support, and inadequate infrastructure hinder widespread adoption.
Government support, investment in research and development, and collaborative efforts between stakeholders are essential to overcome these barriers.
All in all, the integration of robotics in Nigeria’s agricultural sector brings numerous benefits, including increased efficiency, improved productivity, and sustainable farming practices.
Read: Women in Petroleum Engineering in Nigeria: An Overview
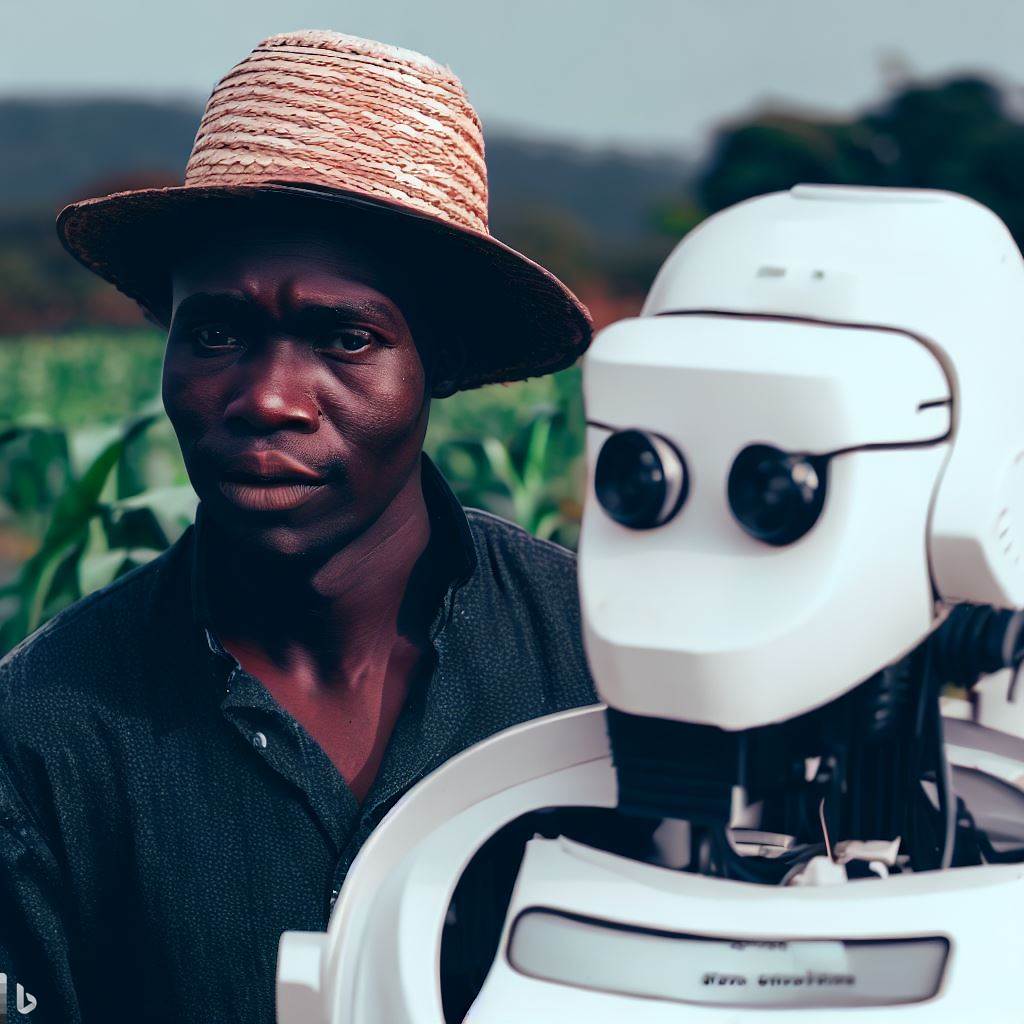

Benefits of Robotic Technology in Agriculture
Robotic technology in agriculture offers various benefits that can revolutionize the sector:
A. Increased efficiency and productivity
- Robots can work continuously without rest, leading to increased efficiency in agricultural operations.
- They can perform tasks at a faster pace than humans, resulting in greater productivity.
- Robotics enables precise and accurate operations, minimizing errors and wastage of resources.
B. Reduction in labor costs
- With the use of robots, the need for human labor in agriculture can be significantly reduced.
- This reduction in labor costs can save farmers’ money and make agriculture more economically viable.
- Robots can perform repetitive and physically demanding tasks, freeing up human workers for more skilled jobs.
C. Improved crop yield and quality
- Robotic technology allows for better monitoring and management of crops, leading to improved yield.
- Robots can precisely apply fertilizers, pesticides, and water, optimizing their usage and minimizing waste.
- They can detect and respond to early signs of plant diseases or nutrient deficiencies, enhancing crop quality.
The integration of robotic technology in Nigeria’s agriculture holds transformative potential.
It addresses food production challenges tied to population growth, elevates farmer livelihoods through cost-efficient labor and enhanced productivity.
Nigeria’s abundant agricultural resources can thrive with robotics, enabling small-scale farmers to rival larger counterparts and boost profitability.
The scope extends beyond crops; automation aids livestock tasks, improving animal welfare and product quality.
Robotics aids climate resilience by monitoring conditions and executing tasks even in harsh weather.
Challenges encompass upfront costs and specialized training, yet government support can surmount these.
Robotic innovation promises employment, entrepreneurship, and a sustainable, secure food future, positioning Nigeria as an agricultural leader.
Read: Role of Petroleum Engineers in Nigeria’s Economy
Challenges and Limitations of Implementing Robotics in Nigerian Agriculture
The integration of robotics into Nigerian agriculture faces multifaceted challenges.
A significant hurdle is the dearth of awareness among farmers and stakeholders regarding the advantages and applications of robotics.
This lack of knowledge breeds skepticism and impedes the acceptance of novel technologies.
Financial constraints and inadequate infrastructure further impede progress. Robotics’ procurement cost is prohibitive for many small-scale Nigerian farmers.
Unreliable power and limited resources hinder the effective utilization of robotics.
Cultural and social barriers compound the difficulties.
Traditional beliefs and hierarchical societal structures deter farmers from embracing unfamiliar technologies, slowing adoption.
Efforts are underway to surmount these obstacles. Awareness campaigns and training initiatives are enlightening farmers about robotics’ potential.
Government collaboration and private sector partnerships aim to make robotics more accessible and affordable.
To overcome cultural resistance, community engagement and evidence-based success stories are vital.
In a nutshell, while challenges persist, integrating robotics can revolutionize Nigerian agriculture, enhancing productivity, food security, and economic growth.
Addressing awareness gaps, resource limitations, and cultural barriers is pivotal for unlocking robotics’ transformative potential.
Read: Petroleum Engineering Internship Opportunities in Nigeria
Potential Future Developments and Opportunities
As the field of robotics continues to advance, there are numerous potential future developments and opportunities in Nigeria’s agricultural sector.
Possibilities for Technological Advancements
- Integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to enhance robotic capabilities.
- Improved sensor technologies for more accurate data collection and analysis.
- Development of autonomous robots capable of performing complex tasks without human intervention.
- Use of drones and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) for crop monitoring and pesticide spraying.
- Application of nanotechnology to create miniaturized robots for targeted delivery of fertilizers and pesticides.
- Advancements in robotic vision and perception systems to increase efficiency in harvesting and crop inspection.
Role of Government and Private Industry in Promoting Robotics in Agriculture
- Government support through funding and favorable policies to encourage research and development in agricultural robotics.
- Collaboration between government agencies, research institutions, and private companies to drive innovation in the sector.
- Investment in training programs to equip farmers and agricultural workers with the necessary skills to operate and maintain robots.
- Creation of test sites and demonstration farms to showcase the benefits of robotic technologies in agriculture.
- Incentives for farmers to adopt robotic systems, such as tax breaks or subsidies for purchasing and implementing robotics solutions.
- Formation of partnerships between local farmers and technology companies to co-create robotics solutions tailored to the specific needs of Nigerian agriculture.
In short, the future of robotics in Nigeria’s agricultural sector holds great promise.
With technological advancements and the support of government and private industry, robots have the potential to revolutionize farming practices and contribute to increased productivity and food security.
It is essential for stakeholders to collaborate and invest in the development and adoption of robotic technologies to reap the benefits they offer.
By embracing robotics in agriculture, Nigeria can position itself as a leader in agricultural innovation and create a sustainable and efficient farming system for the future.
Read: Importance of Continuing Education for Nigerian Robotics Engineers
Success Stories and Case Studies
Here, we will showcase a few successful implementations of robotics in Nigerian agricultural practices and discuss how robotics have positively impacted farmers’ lives and businesses.
Showcase of Successful Implementation of Robotics in Nigerian Agricultural Practices
- In Ogun State, a tomato farming cooperative implemented robots for planting and harvesting, resulting in increased productivity and reduced labor costs.
- A poultry farm in Lagos adopted robotic systems for feeding and cleaning tasks, leading to improved hygiene and efficient resource management.
- At a cassava processing plant in Kogi State, robots were employed to peel and cut cassava, significantly reducing the processing time and improving the quality of the end products.
- In Kwara State, a maize farm implemented autonomous drones for crop monitoring and pest control, resulting in higher crop yields and reduced pesticide usage.
- A fish farm in Edo State employed underwater robots for monitoring water quality and fish health, leading to better disease prevention and improved fish survival rates.
Positive Impact of Robotics on Farmers’ Lives and Businesses
- Increased Efficiency: The use of robotics has streamlined agricultural processes, allowing farmers to accomplish tasks more quickly and efficiently.
- Enhanced Productivity: Automation has enabled farmers to produce higher yields in less time, leading to increased profits and improved livelihoods.
- Reduced Labor Costs: With robots taking over repetitive and labor-intensive tasks, farmers can save on labor costs and allocate their workforce to more skilled and complex jobs.
- Improved Quality: Robotics ensure consistency and precision in tasks such as planting, harvesting, and processing, resulting in higher-quality produce and products.
- Optimized Resource Management: Robots can monitor and analyze data related to soil condition, water usage, and crop health, enabling farmers to make informed decisions and optimize resource allocation.
- Environmental Sustainability: By utilizing robotics, farmers can implement sustainable farming practices, minimize chemical usage, and reduce environmental impact.
- Access to Market: With increased production and improved product quality, farmers can effectively meet market demands and access better market opportunities.
- Skills Development: The adoption of robotics in agriculture requires farmers and workers to acquire new skills, leading to personal and professional growth.
In fact, the implementation of robotics in Nigeria’s agricultural sector has showcased numerous success stories and case studies.
These advancements have positively impacted farmers’ lives and businesses by improving efficiency, productivity, resource management, and product quality.
Robotics have also facilitated environmental sustainability and opened doors to better market access.
As Nigeria continues to embrace technological innovations, the integration of robotics in agriculture promises a brighter future for farmers and the entire agricultural sector.
Read: Universities Offering Robotics Engineering in Nigeria
Conclusion
Robotics plays a significant role in Nigeria’s agricultural sector by increasing efficiency and productivity.
By automating tasks such as planting, harvesting, and monitoring, robots help farmers save time and resources.
Additionally, robotics technology enables precision farming, leading to improved crop yields and reduced waste.
To further promote the adoption and integration of robotic technology in Nigeria’s agricultural sector, it is crucial to increase awareness and provide training opportunities.
Government agencies, research institutions, and private organizations should collaborate to develop initiatives that support the implementation of robotics.
This can include organizing workshops, providing subsidies for farmers to invest in robotic systems, and fostering research in this field.
Moreover, stakeholders should consider the benefits of robotics in terms of sustainability.
By reducing the need for manual labor and optimizing resource utilization, robotics can contribute to a more environmentally friendly agricultural sector.
This aspect should be highlighted in awareness campaigns and policy discussions.
In the end, Nigeria has a great opportunity to leverage robotics technology for the benefit of its agricultural sector.
Embracing this technology can lead to increased productivity, reduced labor costs, and improved sustainability.
It is essential for all stakeholders to come together and actively promote the integration of robotics in Nigeria’s agricultural practices for a prosperous future.
Let us embrace robotics and propel Nigeria’s agricultural sector into the modern age.